Introduction
Few-shot prompting has emerged as a transformative approach in natural language processing (NLP), enabling models to perform tasks with minimal data input. This technique is particularly advantageous in scenarios where data is scarce or costly to procure. By leveraging a handful of examples, few-shot prompting can enhance model performance across a variety of NLP tasks, from text classification to dialogue systems. In this blog post, we will delve into the effectiveness of few-shot prompting, the critical role of prompt engineering, inherent challenges, contextual and multilingual considerations, and the cross-disciplinary applications that demonstrate its versatility.
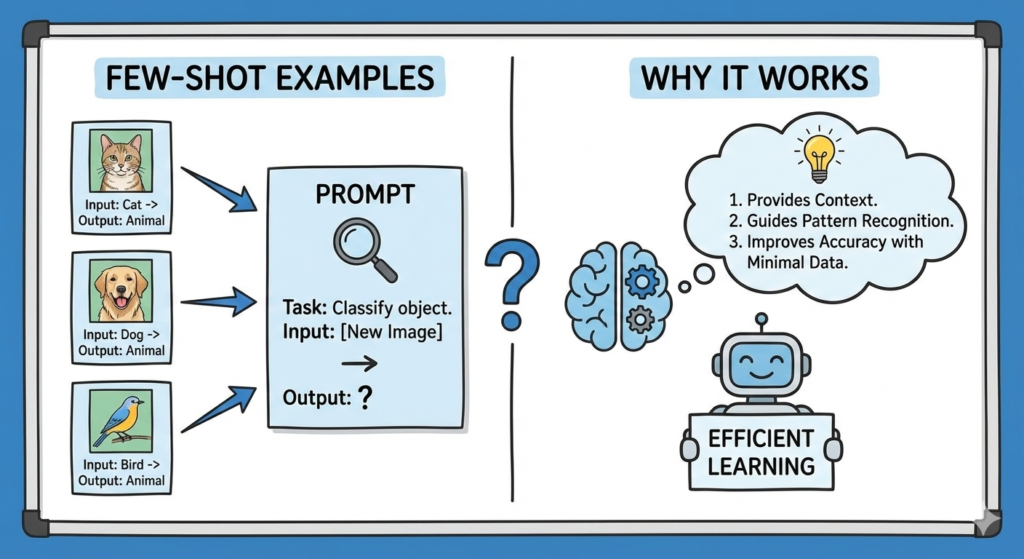
Effectiveness of Few-Shot Prompting
Few-shot prompting techniques have shown remarkable potential in improving model performance despite limited data availability. The central idea is to use a small number of examples to guide the model in understanding and performing the task at hand. This approach is especially beneficial in applications where acquiring large datasets is challenging or impractical.
The effectiveness of few-shot prompting lies in its ability to enhance model generalization and accuracy. By providing a limited set of examples, models can infer patterns and make predictions with surprising accuracy. This capability is crucial for tasks like sentiment analysis, where subtle nuances in language can significantly impact the outcome.
Few-shot prompting’s adaptability extends to a myriad of NLP tasks, including machine translation, named entity recognition, and summarization. Its ability to function with minimal data input makes it a valuable tool in scenarios where traditional data-intensive methods fall short.
Role of Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is a pivotal aspect of few-shot prompting, involving the strategic design of prompts to improve learning outcomes. Crafting effective prompts requires a nuanced understanding of the task and the model’s capabilities.
The design of prompts can significantly influence model performance. A well-crafted prompt can guide the model towards the desired output, enhancing accuracy and adaptability. Researchers are continually exploring innovative prompt designs to maximize the potential of language models in few-shot settings.
Effective prompt engineering can lead to substantial improvements in model performance. By fine-tuning the prompts, researchers can adapt models to various tasks, ensuring they can handle diverse linguistic challenges with minimal examples.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promise, few-shot prompting is not without challenges. Understanding these limitations is crucial for developing robust applications.
One of the significant challenges is the variability in model performance. Few-shot prompting can sometimes yield inconsistent results, especially when dealing with ambiguous or complex tasks. This variability necessitates strategies to stabilize performance across different scenarios.
Few-shot prompting often relies heavily on the context in which the examples are presented. This dependency can lead to issues if the context is not adequately captured or if the model misinterprets the examples.
Contextual and Multilingual Considerations
Incorporating contextual information and addressing multilingual challenges are crucial for the success of few-shot prompting.
Context plays a crucial role in enhancing model predictions. By effectively integrating contextual cues, few-shot prompting can improve the accuracy of predictions, particularly in tasks requiring a deep understanding of nuanced information.
Few-shot prompting must also contend with language-specific issues. Addressing these challenges can broaden the applicability of few-shot techniques across diverse linguistic settings, making them valuable for global NLP applications.
Cross-Disciplinary Applications
Few-shot prompting’s versatility extends beyond traditional NLP tasks, finding relevance in vision-language models and dialogue systems.
In vision-language models, few-shot prompting enables the integration of textual and visual information, allowing models to perform complex tasks such as image captioning and visual question answering with limited data.
Few-shot prompting also plays a critical role in dialogue systems, where it helps models understand and generate human-like responses. This capability is particularly valuable in customer service applications, where models must handle diverse queries with minimal training data.
Conclusion
Few-shot prompting represents a significant advancement in NLP, offering a powerful tool for enhancing model performance with minimal data. Its effectiveness, coupled with strategic prompt engineering, opens new avenues for innovation in both language and vision-language models. However, challenges such as model performance variability and contextual dependencies present opportunities for further research and development. By addressing these challenges and expanding the applicability of few-shot prompting, we can unlock its full potential across a wide range of applications.



